
Mental health check-ups are just as important as physical ones, here is why
When we think about health check-ups, most of us picture blood tests, blood pressure readings, and physical examinations. These are important — […]
Experience MedEx Seamless Care Delivery — 10% OFF on Your First Appointment - Use 'TRYMEDEX' Coupon Code on Checkout


Have you ever experienced unexplained weight gain, mood swings or extreme fatigue? These could be signs of an underlying thyroid issue. The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in your neck that plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the complexities of thyroid health, emphasizing […]

MedEx is a one-stop destination when it comes to medical tourism and digital specialized health care services. MedEx serves as a connector between patients and trusted world-class health service providers.

Have you ever experienced unexplained weight gain, mood swings or extreme fatigue? These could be signs of an underlying thyroid issue. The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in your neck that plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the complexities of thyroid health, emphasizing its significance and offering insights to navigate this often overlooked aspect of well-being.
The thyroid is responsible for producing hormones that regulate metabolism – the process of converting food into energy. Triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) are the primary hormones involved in this process and can significantly impact many bodily functions. Excessive production of thyroid hormone can lead to hyperthyroidism, while insufficient production can result in hypothyroidism, which can lead to complications like heart problems and high cholesterol. Maintaining the delicate hormonal balance of the thyroid is crucial as it plays a pivotal role in overall health.
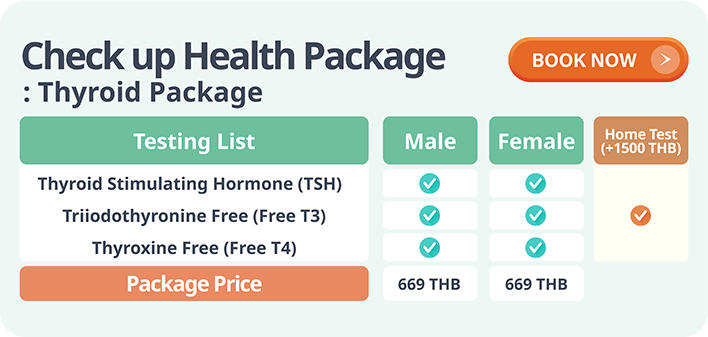
Table of Contents
ToggleThe symptoms of thyroid largely depend on the type of Thyroid you have been affected with. The common symptoms of the thyroid include:
When you visit a doctor for a possible thyroid disorder, your doctor considers symptoms, familial predispositions, and past health conditions during a thorough examination of your medical history. They will then conduct a physical examination, which includes checking your skin, hair, and nails.
If an autoimmune thyroid disorder is suspected, specific antibody tests will be performed to diagnose the problem. The tests will help identify the presence of thyroid antibodies in your blood.
A radioactive iodine uptake (RAIU) test may also be conducted to measure how much iodine your thyroid gland takes up from the bloodstream. This test will help differentiate between different causes of hyperthyroidism.
An ultrasound may also be used to create images of the thyroid gland using sound waves. This will help identify nodules, inflammation, and other structural abnormalities. However, an ultrasound is not required unless there is a goitre. The ultrasound grading system helps assess the goitre and plan further management.
The treatment for thyroid depends on the condition’s type, severity, and underlying causes. There are two main types of thyroid: hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, and one or more of the following treatments are typically used to address them.
Thyroid hormone replacement therapy is the most common treatment for hypothyroidism. This involves taking synthetic thyroid hormone medication, such as levothyroxine, which helps restore normal thyroid hormone levels and alleviate the symptoms of hypothyroidism.
Common thyroid disorders include hypothyroidism, where the thyroid produces insufficient hormones, leading to symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism is characterized by an overactive thyroid, causing symptoms such as weight loss, increased heart rate, and anxiety.
Diagnosis typically involves blood tests measuring levels of thyroid hormones (TSH, T3, T4). Additionally, imaging techniques like ultrasound or thyroid scans may be employed to visualize the thyroid and identify any structural abnormalities.
Treatment options depend on the specific disorder. Hypothyroidism is often managed with synthetic thyroid hormone replacement therapy. Hyperthyroidism may be treated with anti-thyroid medications to regulate hormone production, and in some cases, surgical interventions like thyroidectomy may be recommended. However, proper nutrition, such as iodine and selenium, along with Stress management, regular exercise, and avoiding excessive intake of certain substances (such as soy and excessive iodine) also contribute to overall thyroid well-being.
Yes, some individuals find benefit from complementary approaches such as acupuncture, yoga, and specific herbal supplements. However, consulting with healthcare professionals before incorporating these into a treatment plan is crucial.
Thyroid disorders can impact fertility and may require careful management during pregnancy. Proper thyroid function is essential for the development of the baby’s brain and nervous system. Postpartum thyroiditis, a temporary inflammation of the thyroid after childbirth, is also a consideration.
Yes, Thyroid imbalances can influence mood and mental well-being. Both hypo- and hyperthyroidism have been associated with changes in mood, cognitive function, and emotional well-being. Managing thyroid health is crucial for overall mental and emotional balance.
MedEx collaborates with over 20 JCI-accredited hospitals, offering teleconsultation services with specialists from these reputable institutions. The cost of teleconsultation services starts at 1500 THB and may vary based on the specific specialization of the consulting doctor. Click here to book the online teleconsultation.
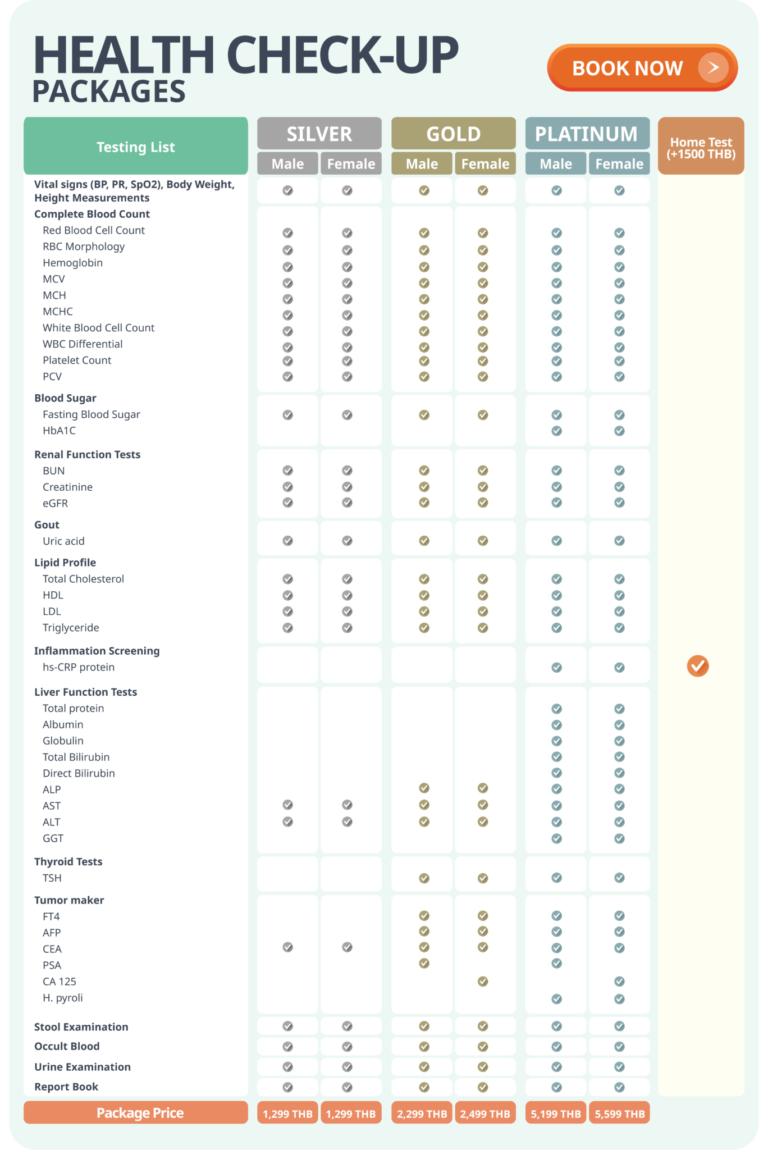
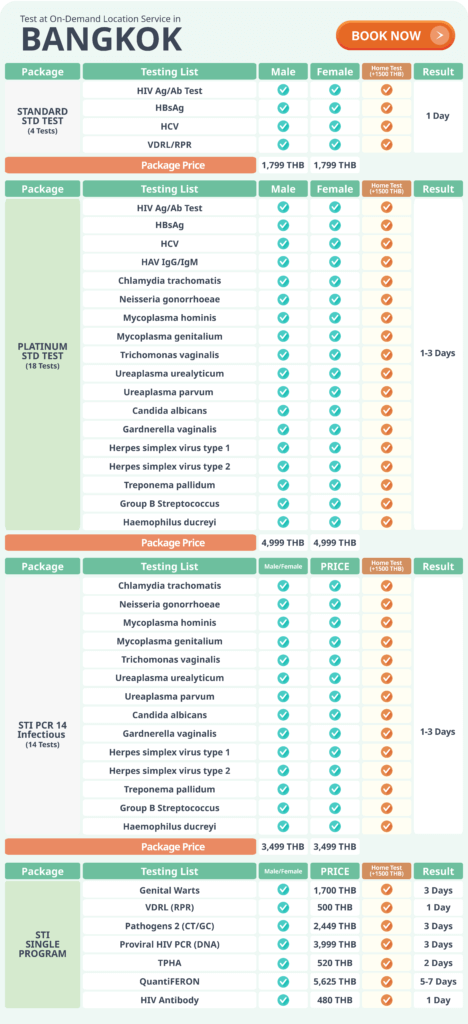

When we think about health check-ups, most of us picture blood tests, blood pressure readings, and physical examinations. These are important — […]

When your doctor orders “routine blood work,” you may later receive a sheet filled with numbers, abbreviations, and reference ranges. For many […]

What exams to expect at every life stage – from your 20s to your 70s and beyond At MedEx, we believe in […]
Find quality services, specialists, procedures and more from the comfort of your home. All you need to do is enter a keyword or phrase describing what you are looking for.
DOWNLOAD MEDEX ONE APP
MedEx decentralizes the care continuum as a one-stop care navigation concierge, transforming the care delivery model through its Pan-Asia provider aggregation platform, primary satellite clinics, telemedicine services, and at-home health care solutions.







MedEx connects you with world-class health care providers across borders, makes medical travel simple, low-cost and transparent and offers premium primary care.


© 2020-25 MedEx Ventures Co., Ltd.
